Introduction to Sub-Datum Memory
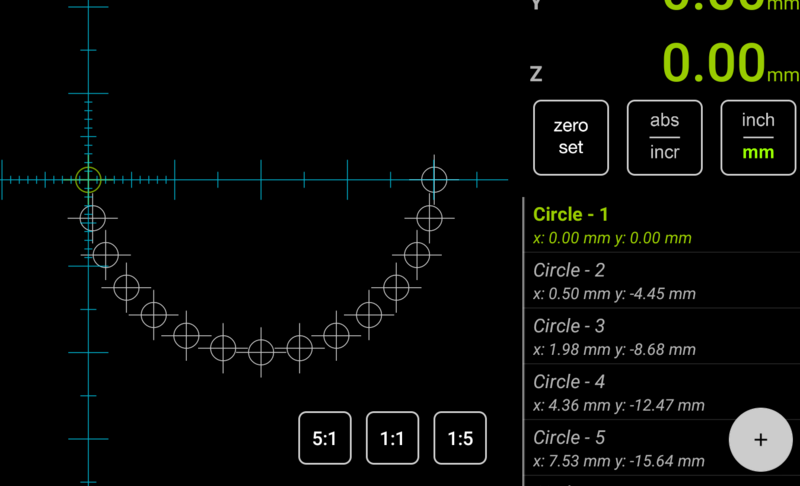
The Saved Sub-Datum Memory is one of the core DRO functions. In a nutshell, sub-datums are coordinates that can be stored into memory and recalled as needed. While this is a very simple context, the Saved Sub-Datum Memory is one of the most powerful features. Besides the simple ability to save a position and then recall it later, the sub-datum memory is used by many standard DRO functions, such as Bolt Hole Circle, Hole Grid, etc. In TouchDRO, this functionality goes much further. Thanks to its graphical display, working with saved coordinates is much more intuitive than in a traditional DRO. Furthermore, using the Graphical Projection View you can easily navigate between saved coordinates and even have TouchDRO automatically select the next sub-datum as you approach it, for a completely hands free operation.
Basic Concepts
The most basic way to use a DRO is to simply move the cutter/workpiece to a desired coordinate. For instance, when you need to drill a few holes you can:
- Move to the location to the first hole
- Zero out the DRO
- Use spot drill to make a dimple for the main drill
- Switch to the jobber drill and drill the hole
- Switch to the countersink and chamfer the hole
- Repeat for the remaining holes
This approach works well for very simple jobs, but when the workpiece is more complex or the number of operations is larger, this approach is very inefficient and error prone. In such a case it's more convenient to first spot drill all relevant locations, then load the jobber drill and drill all holes, etc. This is where sub-datum memory comes into play: after locating each hole for the first operation you can store its location into memory. On the subsequent operations you simply select the next hole and move the table until the DRO reads 0/0 and so on.
Saved Coordinates
Sub-Datum Memory is a fancy name for saved coordinates, but in reality, the concept is very simple: once you indicate a workpiece, you can store any arbitrary coordinate into TouchDRO's memory. At a later time, you can recall that coordinate, and TouchDRO readout will display the distance to its location (which becomes a temporary 0/0 point, or a "sub-datum").
In TouchDRO, there are multiple ways to add coordinates to the sub-datum memory. The most basic approach is to move the cutter to the desired position and press the "Add" button on the Sub-Datum List panel. This will store the coordinate, so it can be used for subsequent operations. For more complex workpieces, it's also possible to predefine coordinates one-at-a-time. FInally, functions such as Bold Hole Circle, Hole Grid, etc. provide a way to create coordinates along the pitch circle or 2 dimensional grid.
These topics are discussed in the "Adding Coordinates to Sub-Datum Memory" sections.
Workspace
TouchDRO's sub-datum memory is organized into workspaces. In a nutshell, a workspace is a virtual container (similar to a computer folder/directory), but in addition to the saved coordinates, it also stores the location of the absolute and incremental origins, location of the guidelines, currently selected units, and the display mode for each visible axis. There are few intended use cases for workspaces:
Multiple Workholding Locations
On larger milling machines, it's common to have multiple workholding devices mounted on the table. For example, you might have more than one milling vise or a vise and a rotary table.
This example works as long as the machine origin stays unchanged. Normally, this would require absolute DRO scales, but TouchDRO scale adapters have few ways to mimic absolute scale functionality. Adapters for capacitive scales can be used with a backup battery, which preserves the machine origin between power downs; adapter for glass/magnetic scales has a provision for homing switches, which can be used to reset machine oring after power loss.
In such situation you can do the following:
- Create a workspace for the vise and set its absolute origin to the left edge of the fixed jaw.
- Create a workspace for the rotary table and set the absolute origin to the table's center.
Next time you use the given work holding device you can simply load the relevant workspace without needing to re-indicate the vise or the rotary table.
Long-Term Storage
You might have some jobs/parts that keep coming back from time to time. Since TouchDRO can store a very large number of workspaces, you can simply store the workspace for this job indefinitely. When needed, you can indicate the part, re-set the absolute origin and all of the stored coordinates will fall into place.
Complex Workpieces
From time to time you might encounter a workpiece with a large number of features. For instance, you might need to drill multiple sets of holes with different diameters, mill pockets, etc. It's very easy to make a mistake such as drilling a wrong hole, etc. In such a situation you might be better off creating a few separate workspaces and grouping the holes/features by their size or the necessary machining operations together.
